Yes, most gasoline-powered chainsaws use mixed gas made from unleaded gasoline and 2-stroke engine oil. The standard mix ratio for modern chainsaws is 50:1, though some older models use 40:1 or 32:1. This fuel mixture lubricates the two-stroke engine, and using straight gas or the wrong ratio can cause severe engine damage or seizure.
What kind of gas do chainsaws use?
Most chainsaw owners eventually face the question: what exactly should I put in my chainsaw’s tank? Understanding the right fuel for your chainsaw is essential for maintaining its performance and extending its lifespan.
Understanding 2-stroke vs 4-stroke engines
Chainsaws predominantly use 2-stroke (or two-cycle) engines rather than 4-stroke engines for several fundamental reasons. In a 2-stroke engine, the combustion cycle completes in just two piston strokes—one up and one down—representing a single crankshaft revolution. Conversely, 4-stroke engines require four piston strokes (two complete revolutions) to complete one combustion cycle.
The primary advantage of 2-stroke engines is their superior power-to-weight ratio. Because 2-stroke engines generate power twice as frequently as 4-stroke engines, they deliver more power per cubic centimeter. This makes them ideal for handheld equipment like chainsaws where weight matters significantly.
Furthermore, 2-stroke engines feature a simpler design without valves, making them lighter and less complex. This translates to less maintenance and lower manufacturing costs—critical factors for tools that endure rough handling in various environments.
Why chainsaws need mixed gas
Unlike 4-stroke engines that have separate chambers for fuel and oil, 2-stroke engines lack a dedicated lubrication system. This absence of an internal oil reservoir creates the necessity for mixed fuel.
In 2-stroke chainsaw engines, the oil mixed with gasoline serves a crucial purpose—it lubricates the internal components, including the piston, cylinder walls, and bearings during operation. Without this oil, these moving parts would quickly wear out due to metal-on-metal contact.
The exact ratio of gas to oil matters tremendously. Most modern chainsaws from manufacturers like STIHL and Husqvarna recommend a 50:1 ratio (50 parts gasoline to 1 part oil). This precise mixture ensures adequate lubrication without compromising combustion efficiency or creating excessive smoke.
The quality of both components in your mix is equally important. Leading manufacturers recommend:
- Gasoline with a minimum octane rating of 89-90
- High-quality 2-stroke engine oil that meets TC classification requirements
Using lower octane fuel than recommended can cause serious engine damage through improper combustion and increased heat.
What happens if you use regular gas
Running a chainsaw on straight gasoline (without oil) is one of the most damaging mistakes an owner can make. Within minutes of operation, the engine will become extremely hot due to inadequate lubrication.
The consequences progress rapidly:
- Loss of lubrication leads to metal-on-metal contact between critical components
- Increased friction causes overheating and expansion of parts
- The piston and cylinder develop scoring and increased clearances
- In severe cases, complete engine seizure occurs—often resulting in catastrophic damage
Even if you realize your mistake quickly, running a chainsaw even briefly on unmixed gas can significantly shorten its lifespan. After such an incident, immediate action is necessary—drain the fuel tank, refill with properly mixed fuel, and check for abnormal noises or vibration.
Beyond using no oil at all, using an improper ratio can cause problems too. Too much oil causes carbon buildup, excessive smoke, and poor performance, while too little oil risks engine damage similar to using straight gas.
For optimal chainsaw performance and longevity, always follow the manufacturer’s fuel recommendations precisely—your saw’s life depends on it.
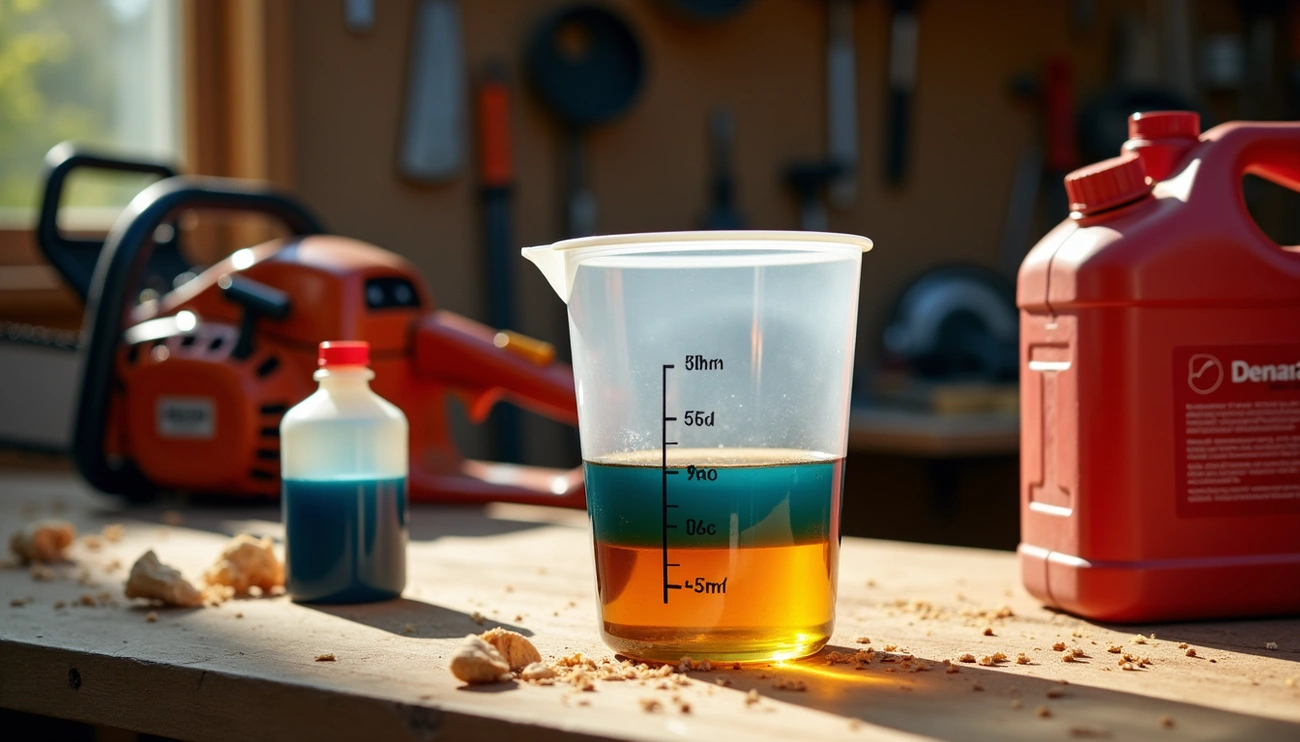
The correct chainsaw gas mix ratio
Getting the fuel mixture right for your chainsaw isn’t just about performance—it’s about protecting your investment. The gas-to-oil ratio can significantly impact your chainsaw’s lifespan, making it essential to understand exactly what these numbers mean and how to mix them correctly.
What is the 50:1 ratio?
First of all, the 50:1 ratio represents the proportion of gasoline to two-stroke oil in your chainsaw’s fuel mixture. This ratio translates to 50 parts gasoline to 1 part oil, creating a 2% oil concentration. Most modern chainsaws from major manufacturers like STIHL and Husqvarna recommend this specific ratio.
When you see 50:1 on your chainsaw’s manual or oil bottle, it means for every 50 units of gas, you need 1 unit of oil. For instance, 5 liters of gas would require 100 ml of two-stroke oil. This precise proportion ensures your chainsaw receives adequate lubrication without compromising engine performance or creating excessive smoke.
Interestingly, this ratio wasn’t established arbitrarily. According to experts, the 50:1 ratio offers optimal cooling properties through the higher volatility of gas compared to oil. Moreover, modern chainsaws with tighter design clearance tolerances require less oil film thickness, making this leaner mixture ideal for today’s equipment.
How to calculate the right mix
Calculating the proper chainsaw gas mix involves simple math, but precision matters. Here’s a breakdown of common measurements for a 50:1 ratio:
| Gasoline Amount | Oil Required (50:1) |
|---|---|
| 1 Gallon | 2.6 oz |
| ½ Gallon | 1.3 oz |
| 1 Liter | 20 ml |
| 5 Gallons | 12.8 oz |
For example, to mix one gallon of fuel at a 50:1 ratio, add 2.6 ounces of two-stroke oil to one gallon of gas. Many manufacturers make this process easier by selling pre-measured bottles designed for specific quantities—typically one gallon.
When making your mix, always start by pouring half the intended amount of gasoline into your container, then add all the oil, and finally add the remaining gasoline. This method ensures thorough mixing. Additionally, shake the container vigorously to properly blend the components.
Common mix ratio mistakes to avoid
Several common errors can lead to significant chainsaw problems. Among these, using the wrong ratio tops the list of potentially damaging mistakes.
Using too little oil in the mixture (less than the recommended 50:1 ratio) can cause your chainsaw to overheat and sustain permanent internal damage. The insufficient lubrication leads to metal-on-metal contact and excessive wear.
Conversely, adding too much oil (creating a mixture richer than 50:1) often results in poor engine performance, carbon buildup on engine internals, excessive smoke, and starting difficulties. Some users mistakenly believe that “more oil is better,” but this misconception can actually harm your equipment.
Another frequent error involves small calculation mistakes when mixing small quantities of fuel. As pointed out by Husqvarna, “Small errors can influence the ratio of the mixture drastically when mixing small quantities of fuel”. To avoid this, measure oil carefully using precise measuring tools rather than estimating.
Notably, some older chainsaw models might require different ratios like 40:1 (3.2 oz of oil per gallon) or even 32:1 (4.0 oz per gallon). Always consult your owner’s manual for the manufacturer’s specific recommendation. Furthermore, using old gas can ruin your fuel mix, as gasoline begins breaking down after just a few weeks.
Using the incorrect type of oil represents another critical mistake. Only use oil specifically designed for air-cooled two-stroke engines that meets TC classification requirements. Using automotive oil or oil designed for water-cooled engines can cause serious damage to your chainsaw.
How to mix gas and oil for chainsaw use
Properly mixing fuel for your chainsaw isn’t just about knowing the right ratio—it’s about executing the process correctly. Since chainsaws take mixed gas, understanding exactly how to prepare that mixture can make the difference between smooth operation and engine damage.
Step-by-step mixing instructions
Creating the perfect chainsaw gas mix requires a methodical approach:
- Begin by measuring the correct amount of gasoline—typically mid-grade unleaded with a minimum octane rating of 89.
- Pour half of your measured gasoline into an approved fuel container first.
- Add the entire amount of two-stroke oil to the container (for a 50:1 mix, that’s 2.6 ounces of oil per gallon of gas).
- Close the container securely and shake it thoroughly to blend the oil with the half-portion of gas.
- Subsequently, add the remaining gasoline to reach your desired total volume.
- Seal and shake vigorously for about 30 seconds to ensure proper mixing.
Remember, small errors in measurement can drastically affect the mixture when working with smaller quantities, so precision matters greatly.
Choosing the right container
The container you select for mixing plays a crucial role in both safety and convenience:
Always use an approved gasoline container specifically designed for fuel storage. The leading cause of contaminated fuel is dirty containers, hence using a dedicated, clean container is essential.
Many manufacturers offer specialized options that simplify the mixing process. STIHL, for instance, sells combination canisters specifically designed for this purpose. These specialized containers often feature:
- No-spill valves to reduce spillage and evaporation
- Separate compartments for oil and gas
- Built-in measuring systems
For smaller quantities, transparent containers allow you to see how full they are during filling, preventing overflow onto floors or equipment.
Shaking and storing the mix properly
Once mixed, proper handling remains critical:
Shake the fuel mixture vigorously by hand before each use to ensure oil hasn’t separated from the gasoline. Inadequate mixing can lead to oil floating on top, which won’t provide proper lubrication.
As for storage, primarily note that mixed fuel has a limited shelf life. Never store two-stroke fuel mix for more than 30 days. Within this timeframe, the ethanol in the fuel can bind with moisture from the air, causing the oil and gasoline to separate.
When storing your mixture:
- Keep it in a cool, dry place away from ignition sources
- Use the mixture within a month to ensure freshness and effectiveness
- Before refueling, always clean the fuel cap and surrounding area to prevent contamination
Fundamentally, maintaining these practices ensures your chainsaw receives the proper lubrication it needs while protecting your investment for years to come.
Best practices for fueling your chainsaw
Refueling your chainsaw involves more than just pouring gas into a tank—it requires careful attention to safety and proper technique. After all, since chainsaws take mixed gas, proper handling becomes even more critical for both equipment longevity and personal safety.
Safety tips before refueling
First and foremost, never refuel a running or hot chainsaw. Always shut off the engine completely and allow it to cool for at least five minutes before attempting to refuel. This cooling period helps prevent accidental ignition that could lead to serious injury or fire.
When handling chainsaw fuel mix, maintain a safe distance from any naked flames—ideally at least 20 feet away from any ignition sources. Particularly important is the prohibition against smoking during the refueling process. In fact, fire safety should be your primary concern whenever working with chainsaw fuel.
How to avoid spills and contamination
To minimize spills and contamination when refueling:
- Use approved containers specifically designed for fuel storage
- Employ a funnel or flexible hose when pouring fuel to prevent spills
- Hold the nozzle directly into the saw to avoid spillage
- Wear gloves to protect your hands and keep them clean
- Wipe the saw dry of any spilled fuel before starting it
Tipping the saw slightly on its side often provides the best angle for filling both the fuel tank and the chain oil reservoir without overflow. Nevertheless, be prepared to immediately clean any drips that occur despite your precautions.
When and where to refuel
Timing and location matter considerably in chainsaw refueling. Always refuel in well-ventilated spaces to prevent vapor buildup. Maintain proper distance—at least 10 feet from where you’ll restart the saw and resume cutting.
The chainsaw’s fuel tank should never be filled while the engine is hot, as there’s significant risk of fire if the fuel mix overflows. Certainly worth noting is that refueling should occur at least 3 meters from your working area.
Carefully close the fuel cap after refueling so any overpressure dissipates gradually, ensuring no fuel sprays out unexpectedly. Indeed, proper cap closure represents one of the most overlooked yet critical aspects of safe refueling.
Storage and shelf life of mixed fuel
The shelf life of your chainsaw fuel mix is often overlooked yet remains critically important for equipment performance. Proper storage practices can mean the difference between a quick start and frustrating repairs.
How long does mixed gas last?
The lifespan of mixed chainsaw fuel is surprisingly short. STIHL currently recommends not using fuel older than 60 days, and preferably no longer than 30 days, even with stabilizer added. Similarly, Husqvarna specifies a maximum storage time of just 1 month for gasoline and ready fuel mixtures. This short timeframe exists because ambient oxygen and moisture infiltrate the fuel, potentially attacking essential components like antioxidants and corrosion protection.
Yet not all fuel options share this limitation. Pre-mixed commercial products like STIHL MotoMix contain no ethanol and can last up to two years, making them valuable alternatives for occasional users.
Signs your fuel has gone bad
Watch for these indicators of degraded chainsaw fuel mix:
- Resinous “gum” formation from evaporated fuel
- Separation of oil and gasoline, especially with ethanol-containing fuels
- Engine refuses to start or won’t rev properly
- Primer bulb functioning issues
- Foul smell in the gas tank
- Excessive smoke, particularly white smoke from the exhaust
Once fuel separates, you can’t restore proper lubrication by shaking, as the oil distribution remains uneven.
Using fuel stabilizers for longer storage
Fuel stabilizers work by slowing the chemical reactions that cause gasoline deterioration. These additives can effectively:
- Prevent varnish formation in the carburetor
- Protect against corrosive condensation
- Eliminate cold start issues after storage
For seasonal equipment storage, either drain the tank completely or add stabilizer then run the engine briefly to circulate it throughout the system. Quality stabilizers can extend fuel life significantly, although manufacturers still recommend refreshing fuel within 30-60 days for optimal performance.
Conclusion
Proper fuel mixing stands as perhaps the most crucial aspect of chainsaw maintenance and operation. Throughout this guide, we’ve seen why chainsaws take mixed gas and how this specific combination protects your equipment. The 50:1 ratio recommended by major manufacturers like STIHL and Husqvarna isn’t arbitrary but rather carefully calculated to provide optimal lubrication while maintaining efficient combustion.
Remember, using straight gas even briefly can cause catastrophic damage to your chainsaw’s engine. Similarly, incorrect ratios—whether too much or too little oil—will undoubtedly lead to performance issues and potentially expensive repairs. Accuracy matters tremendously when measuring your components, especially with smaller quantities where minor errors significantly impact the final mixture.